Chickenpox is a common illness that mostly affects children, but adults can catch it too. While usually mild, it can be uncomfortable and sometimes lead to complications. Let’s look at some of the primary chickenpox causes, its symptoms, how it spreads, and the best ways to prevent and treat chickenpox.
What Causes Chickenpox?
Chickenpox is caused by the varicella-zoster virus. This virus is highly contagious and spreads easily from person to person, especially among children. If you’ve never had chickenpox or the varicella vaccine, you can catch the virus through:
- Coughing, or sneezing from an infected person
- Touching the rash, or blisters
- Sharing items like clothing, bedding, or towels
Once infected, it usually takes 10 to 21 days for symptoms to appear, and if you’re wondering, is chickenpox contagious? Yes, it is — and the virus can spread to others even before the rash becomes visible.
Chickenpox Symptoms: What to Look For
Chickenpox symptoms usually start with a few mild signs before the rash shows up. Here’s what you or your child might notice:
- Mild fever, and feeling tired
- Loss of appetite
- Headache
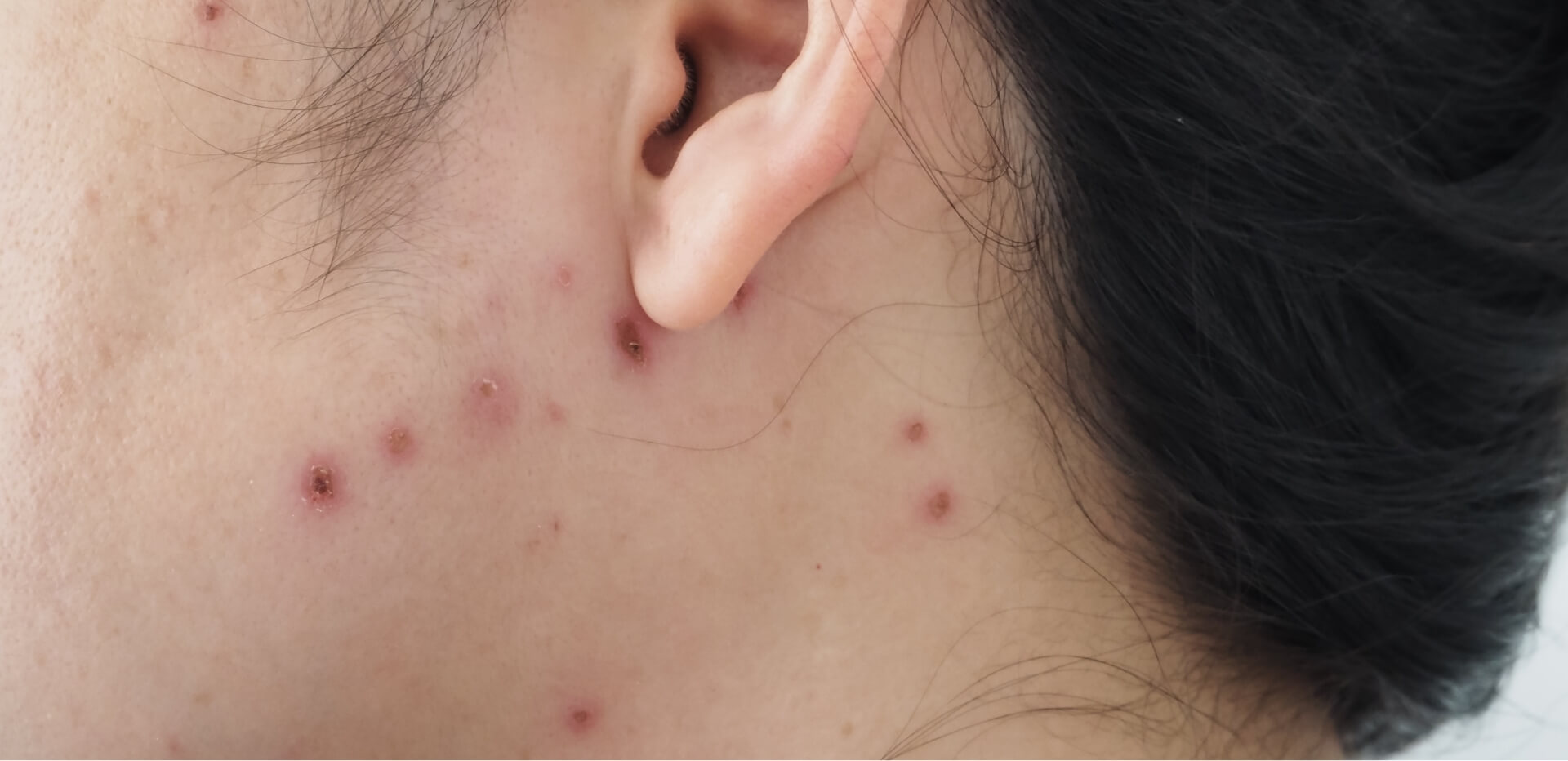
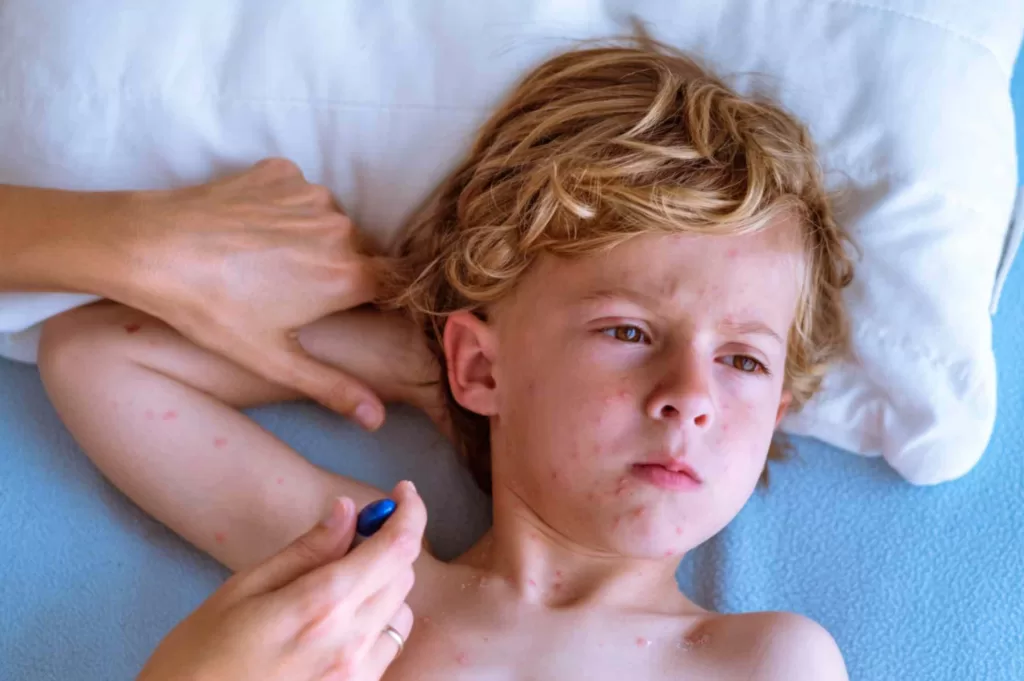
- After 1–2 days: an itchy red rash with spots that turn into blisters, then scab over
The rash usually starts on the chest, back, or face and can spread across the body. Some people only get a few spots, while others can have hundreds.
The illness typically lasts 7–10 days, and most people recover fully without serious problems.
Is Chickenpox Dangerous?
For most healthy children, chickenpox is mild. But for babies, pregnant women, adults, or people with weak immune systems, it can be more serious.
Possible complications include:
- Skin infections from scratching
- Lung problems (pneumonia)
- Brain swelling (rare but serious)
- Shingles later in life (the same virus can become active again years later)
That’s why it’s important to take chickenpox seriously, even if it seems like a childhood rite of passage.
How to Prevent Chickenpox
The best way to prevent chickenpox is through vaccination. The varicella vaccine is safe and effective. It is usually given in two doses, starting at around 12 months of age.
People who haven’t had chickenpox or the vaccine, especially healthcare workers, teachers, and parents of young children, should consider getting vaccinated.
Other ways to prevent spread include:
- Keeping infected people at home until all blisters have crusted over
- Washing hands often
- Not sharing personal items
- Covering the mouth, and nose when sneezing, or coughing
Chickenpox Treatment: What Can You Do?
There’s no specific cure for chickenpox, but you can treat the symptoms and make yourself (or your child) more comfortable. Here are some chickenpox treatment tips:
- Rest, and stay hydrated
- Paracetamol (not ibuprofen) for fever, or pain
- Calamine lotion, or cooling gels for itching
- Loose clothing to avoid irritation
- Cut nails short to reduce scratching, and lower infection risk
In some cases, professionals may prescribe antiviral medicines if you’re at higher risk of complications. Don’t give aspirin to children — it can lead to a serious condition called Reye’s syndrome.
Stay One Step Ahead: Protect Your Family from Chickenpox!
So, if you’re a parent or teacher or planning to travel, the varicella vaccine offers vital protection against chickenpox. Our trained staff provide safe, professional vaccination services for children and adults. Don’t wait until it spreads — book your appointment today, and keep your loved ones protected from this itchy, uncomfortable illness.