According to the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA), there were 73 travel‑associated chikungunya cases reported in England between January and June 2025, compared to just 27 cases during the same six‑month period in 2024. This represents the highest number recorded for that timeframe to date, confirming a significant rise in imported chikungunya cases in the UK.
Chikungunya is a viral illness that is most common in tropical and subtropical areas but can affect anyone travelling abroad. Knowing the causes of chikungunya fever and understanding who is most at risk is an important step in staying safe.
What Causes Chikungunya?
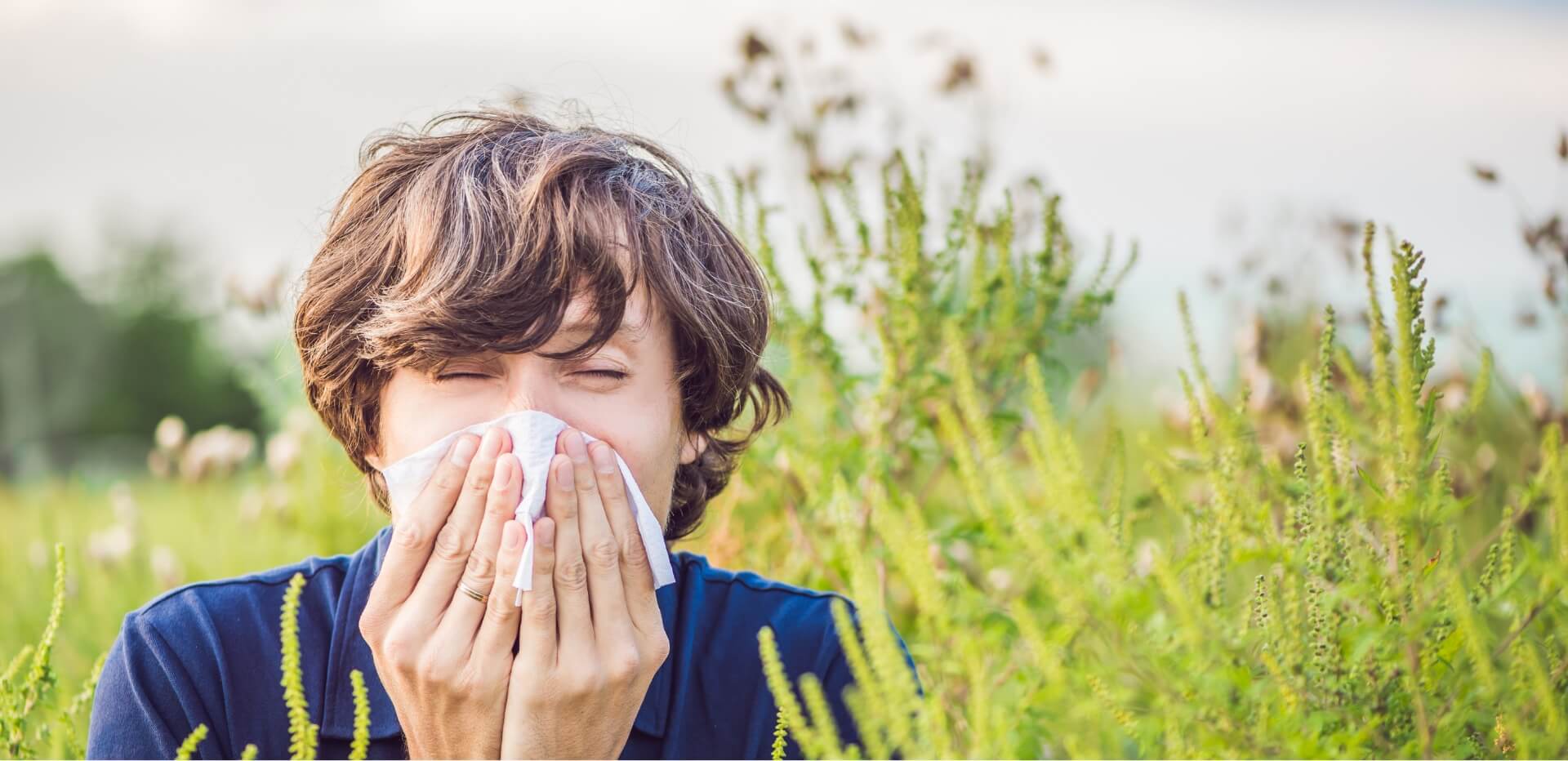
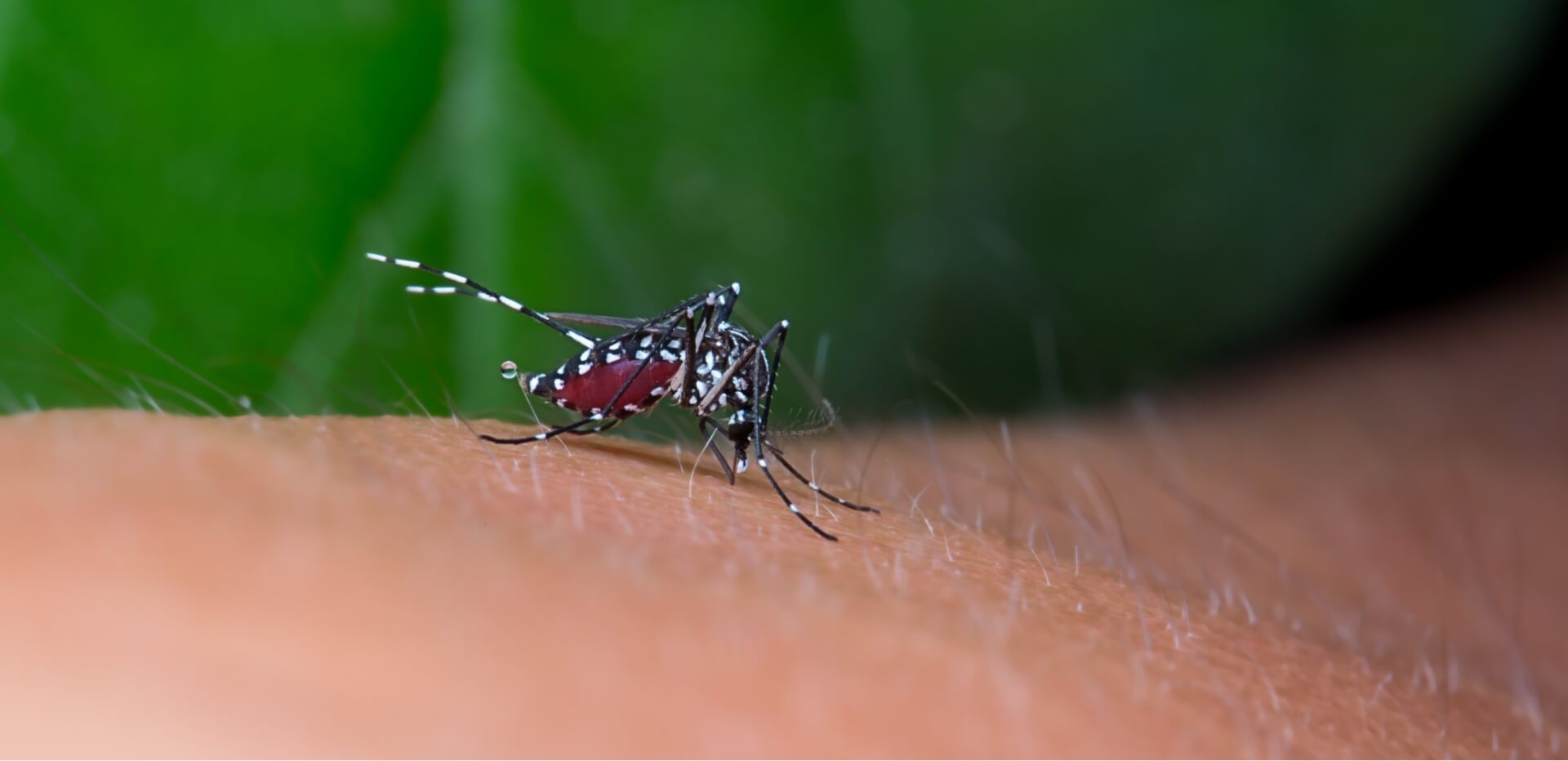
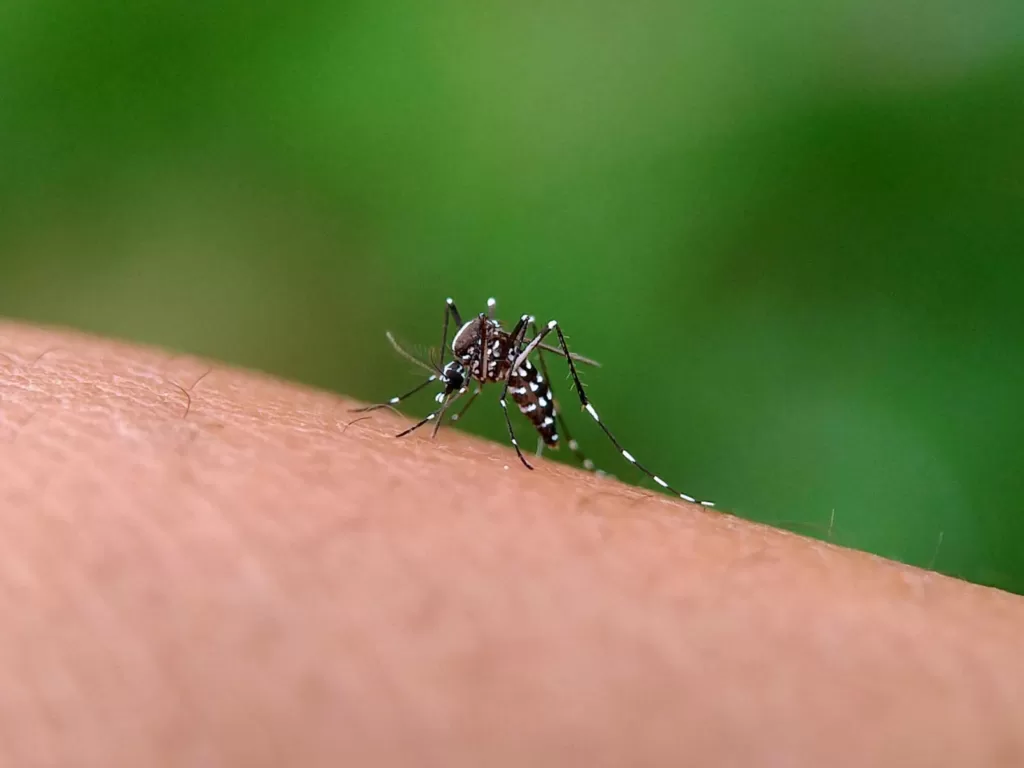
The main cause of chikungunya fever is the chikungunya virus, which is spread to people through mosquito bites. The Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes are responsible for transmitting this infection. These mosquitoes usually bite during the day, especially in the early morning and late afternoon.
When an infected mosquito bites a person, the virus enters the body and begins to multiply, leading to illness. This is the simple answer to what causes chikungunya in humans. Unlike some other illnesses, it is not spread directly from person to person, which means you cannot catch it by touching or being close to someone who has it.
How Is Chikungunya Transmitted?
Many people wonder, “How is chikungunya transmitted?” Understanding how the virus is transmitted helps in lowering the chances of infection. Mosquitoes become carriers when they bite a person who already has the virus in their blood. The insect then passes the virus to another person when it bites again.
The spread often increases in areas with standing water, such as puddles, buckets, or old tyres, where mosquitoes breed. Travellers to countries with outbreaks are also at greater risk of being bitten by an infected mosquito.
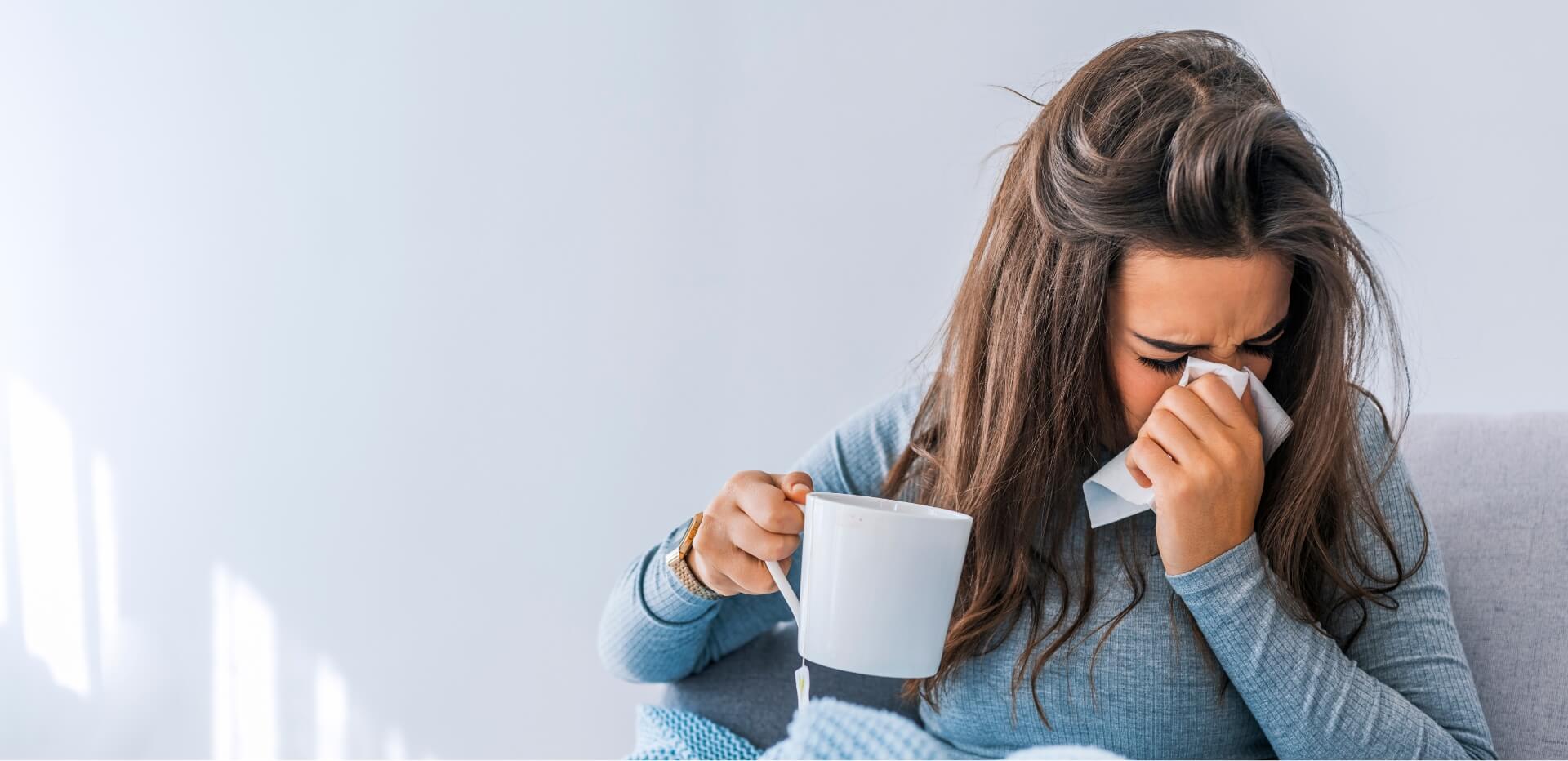
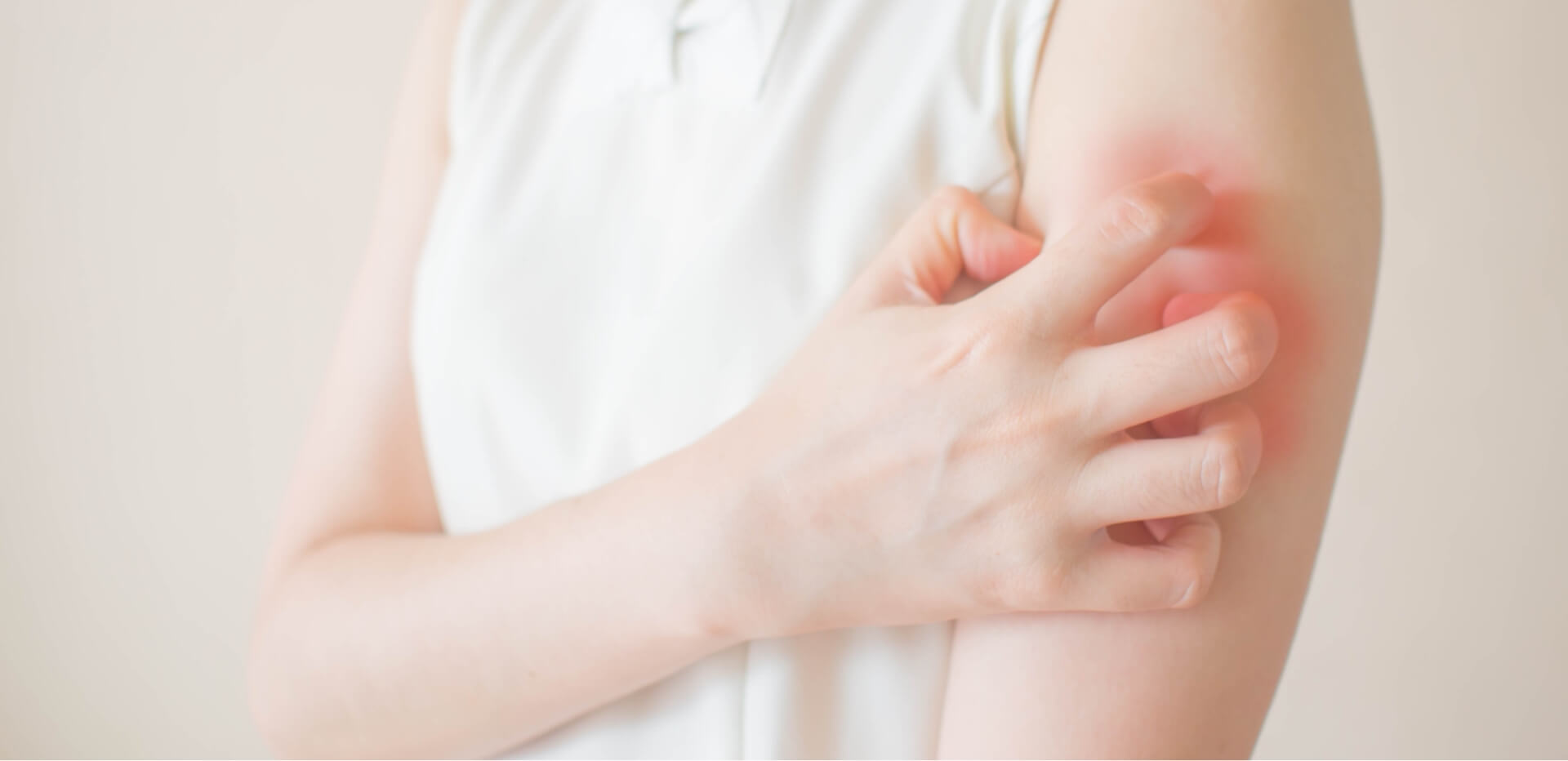
Symptoms of Chikungunya Disease
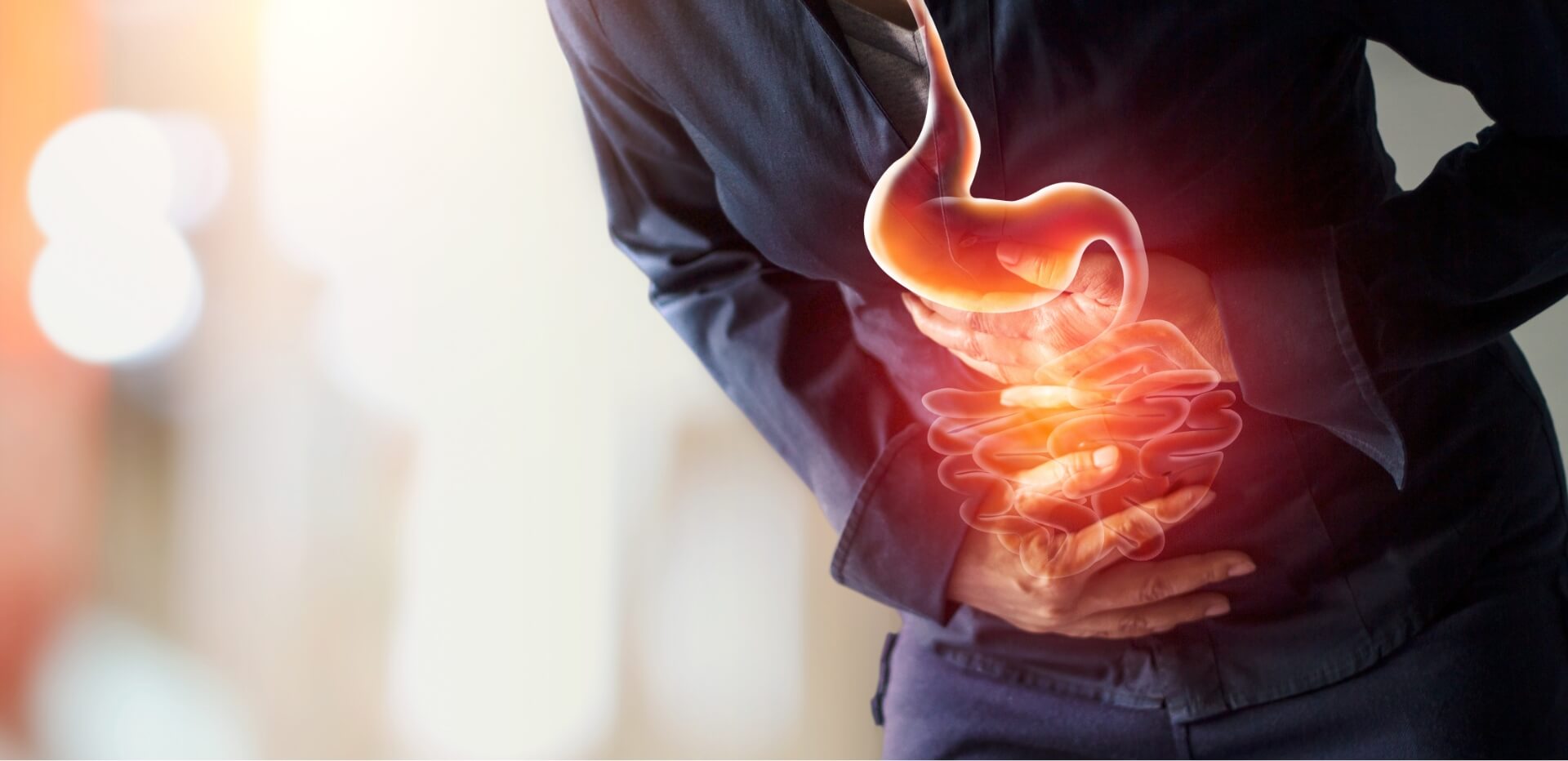
After being bitten by an infected mosquito, symptoms of chikungunya disease usually appear within 4 to 8 days. The illness often starts suddenly with high fever and severe joint pain, which can be very uncomfortable. Other common signs include:
- Headaches
- Muscle pain
- Rash
- Fatigue
- Nausea
The joint pain can sometimes last for weeks or even months, making it one of the most difficult parts of the illness for many people.
Chikungunya Risk Factors
Certain people are more likely to experience severe effects of chikungunya. The main chikungunya risk factors include:
- Travelling to or living in regions where the virus is common
- Being bitten often by mosquitoes due to lack of protection
- Older adults, who may have weaker immune systems
- People with long-term health conditions, such as diabetes or high blood pressure
- Pregnant women, as there is a risk of passing the virus to newborns in rare cases
Chikungunya Virus Prevention
The best way to reduce your risk of infection is by combining the chikungunya vaccination with protective measures. While a chikungunya vaccine is available through private travel clinics, you should also take steps to avoid mosquito bites for extra protection. Useful measures include:
- Using mosquito repellent regularly
- Wearing long-sleeved clothing when possible
- Sleeping under mosquito nets if you are in an affected region
- Avoiding areas with standing water where mosquitoes breed
- Keeping windows and doors closed or using screens
- By reducing mosquito exposure, you can greatly lower your chances of being infected.
Get Protection and Guidance from Our Experts
If you are planning to travel to an area where chikungunya is common, it is important to take preventive steps. Our experts at Touchwood Pharmacy can provide advice on travel health, mosquito protection, and other vaccines you may need before your trip.
Book your appointment with our experts at Touchwood Pharmacy for trusted guidance, personalised travel health advice, and protection against infections, So you can travel with peace of mind.